The oblique occipital sinus – implications in posterior fossa approaches
Carlos Candanedo, Samuel Moscovici, Andrew H. Kaye, Sergey Spektor
Department of Neurosurgery, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
Department of Surgery, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Article Information
- Received: 6 March 2020
- Accepted: 12 April 2020
Keywords
- Oblique occipital sinus
- Vestibular schwannoma
- Retrosigmoid approach
- Cerebellopontine angle
- Occipital sinus
Abstract
The retrosigmoid craniotomy is the standard approach to resect pathologies in the cerebellopontine angle (CPA). Following the craniotomy, the dura mater is opened in the inferolateral direction and the basal cistern arachnoid is dissected in order to release pressure by the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the foramen magnum, so that the CPA compartment can be approached with minimal retraction of the cerebellum.
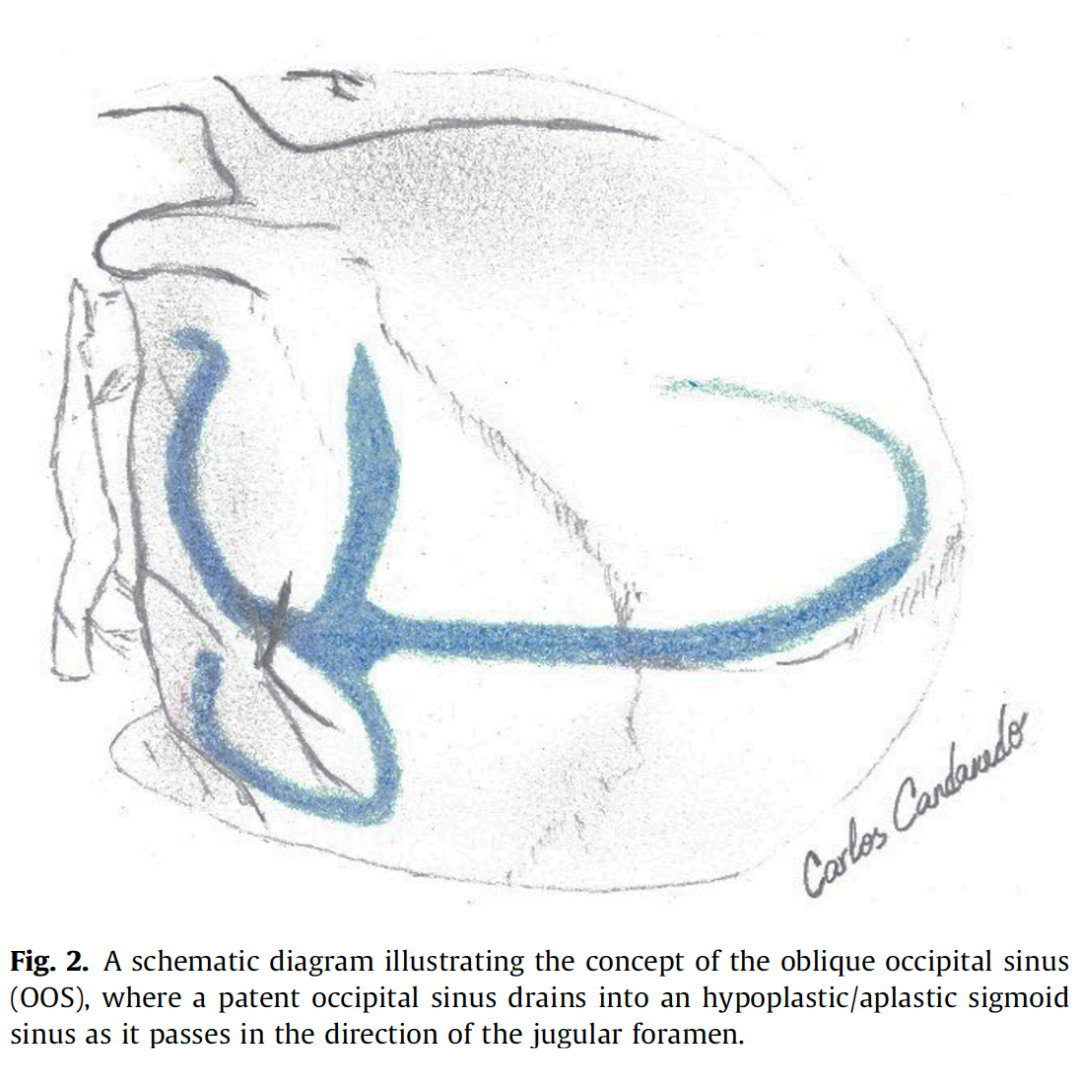
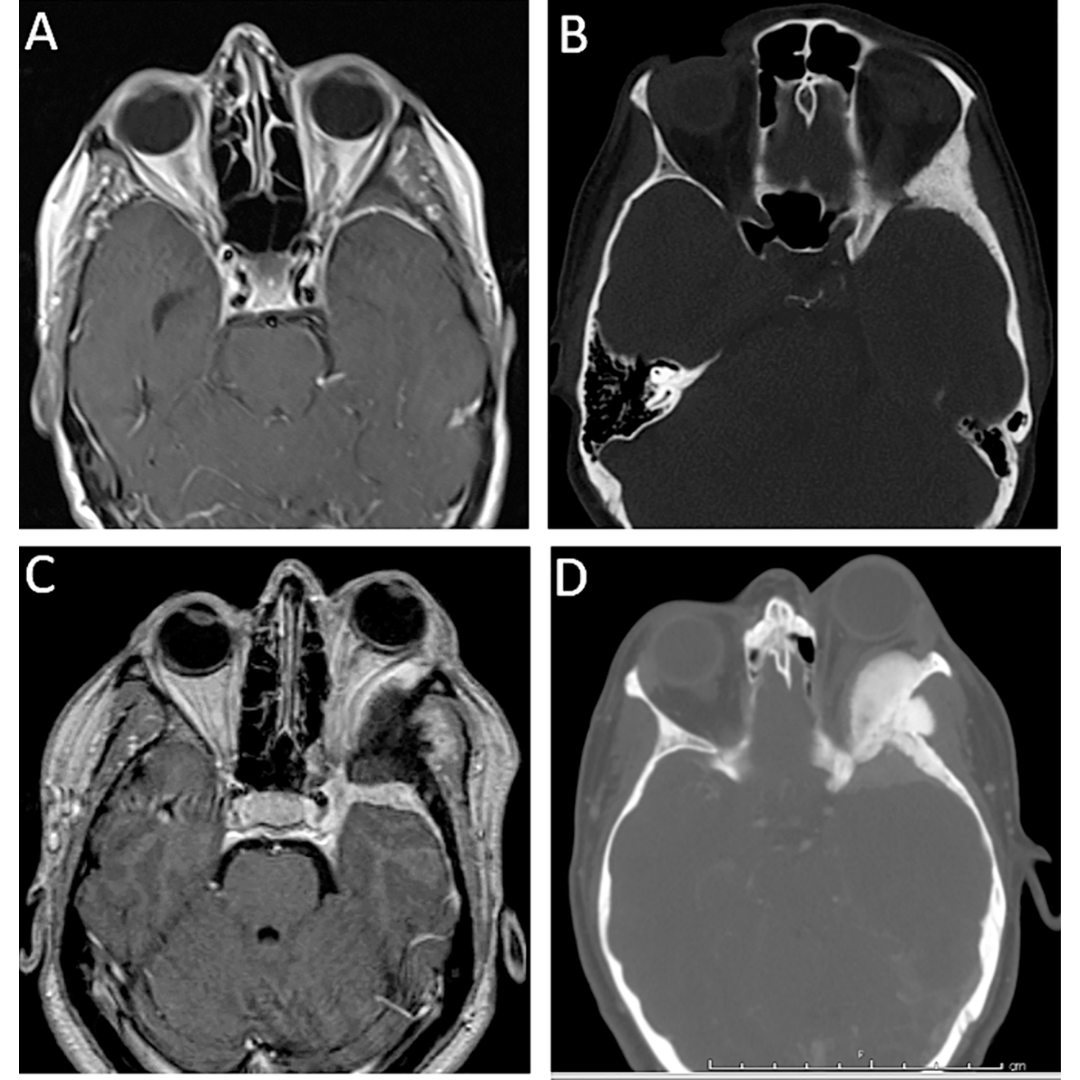
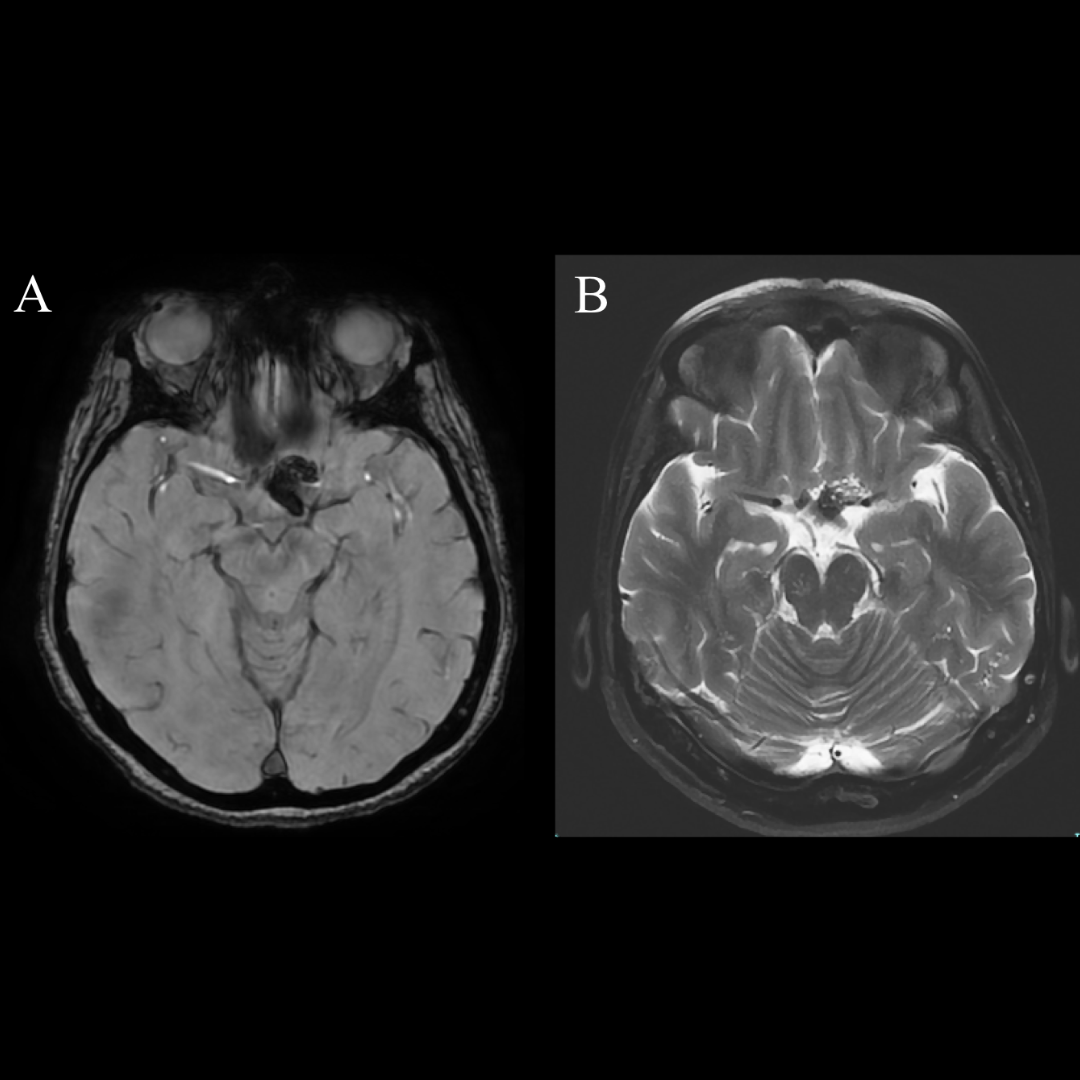
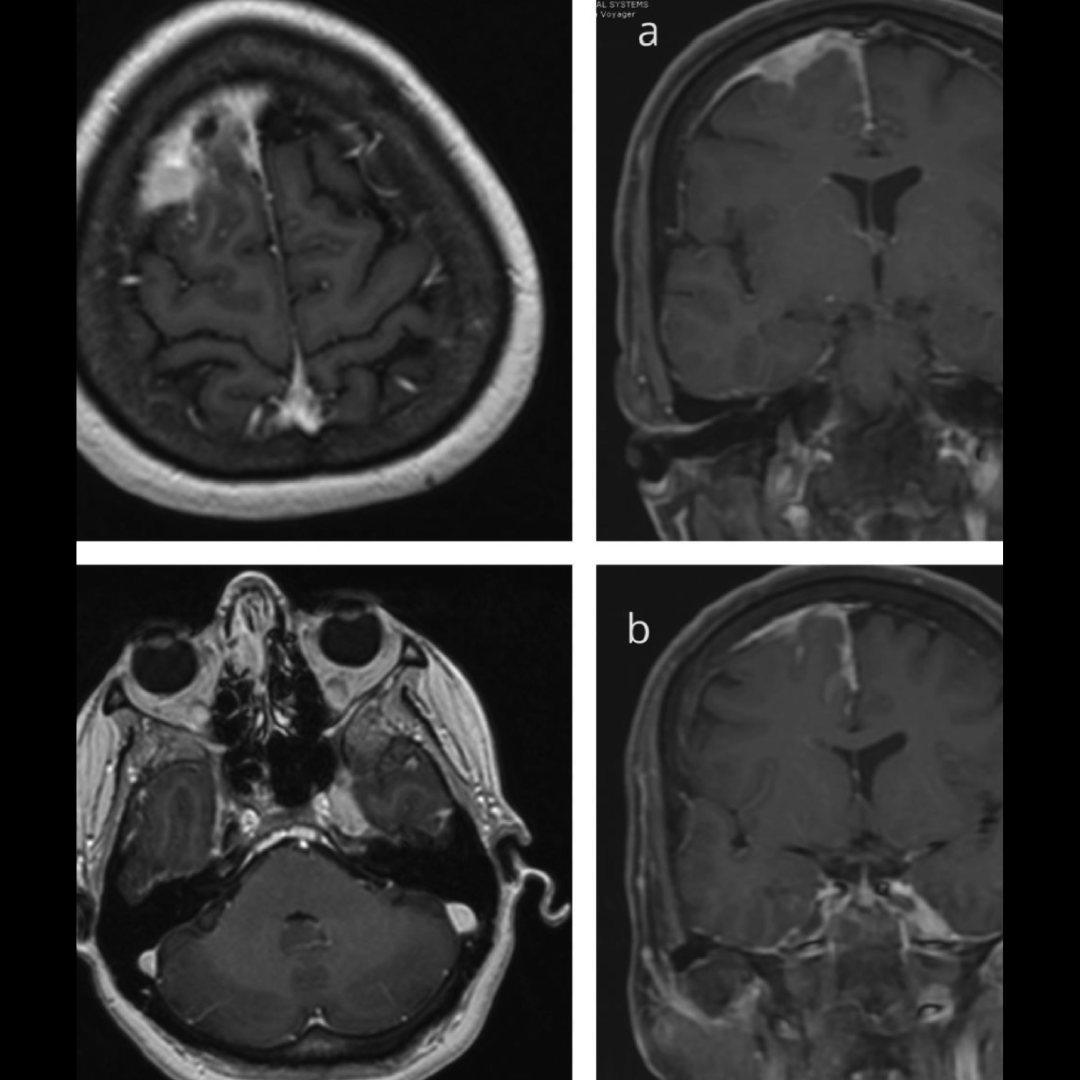
We report two patients, both with vestibular schwannoma, in whom preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed unusual large oblique occipital sinus (OOS) draining laterally into the sigmoid sinus-jugular bulb junction. The sinuses were preserved intact while the dura mater was opened for CSF release.
Careful preoperative imaging is essential prior to posterior fossa lesion approaches in order to evaluate the persistency of an OOS, especially in a retrosigmoid approach. Inadvertent OOS damage might result in not only significant bleeding during dural opening, but also air embolism or venous hypertension, if the contralateral sigmoid sinus is small or absent.