Combination Treatment with Intravenous Tigecycline and Intraventricular and Intravenous Colistin in Postoperative Ventriculitis Caused by Multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Authors:
Cezar J. Mizrahi, Shmuel Benenson, Samuel Moscovici, Carlos Candanedo, Mony Benifla, Sergey Spektor
Affiliations:
- Neurosurgery, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
- Neurosurgery, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center
- School of Medicine, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel
Corresponding Author:
Sergey Spektor (sergeyspektor@gmail.com)
Disclosures can be found in the Additional Information section at the end of the article.
Abstract
Nosocomial infections with multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens are a life-threatening complication in neurosurgery. An MDR Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) central nervous system (CNS) infection following neurosurgery has been previously reported and was treated with relative success using intraventricular and/or intravenous (IV) colistin, IV tigecycline, or IV colistin-rifampicin combination therapy.
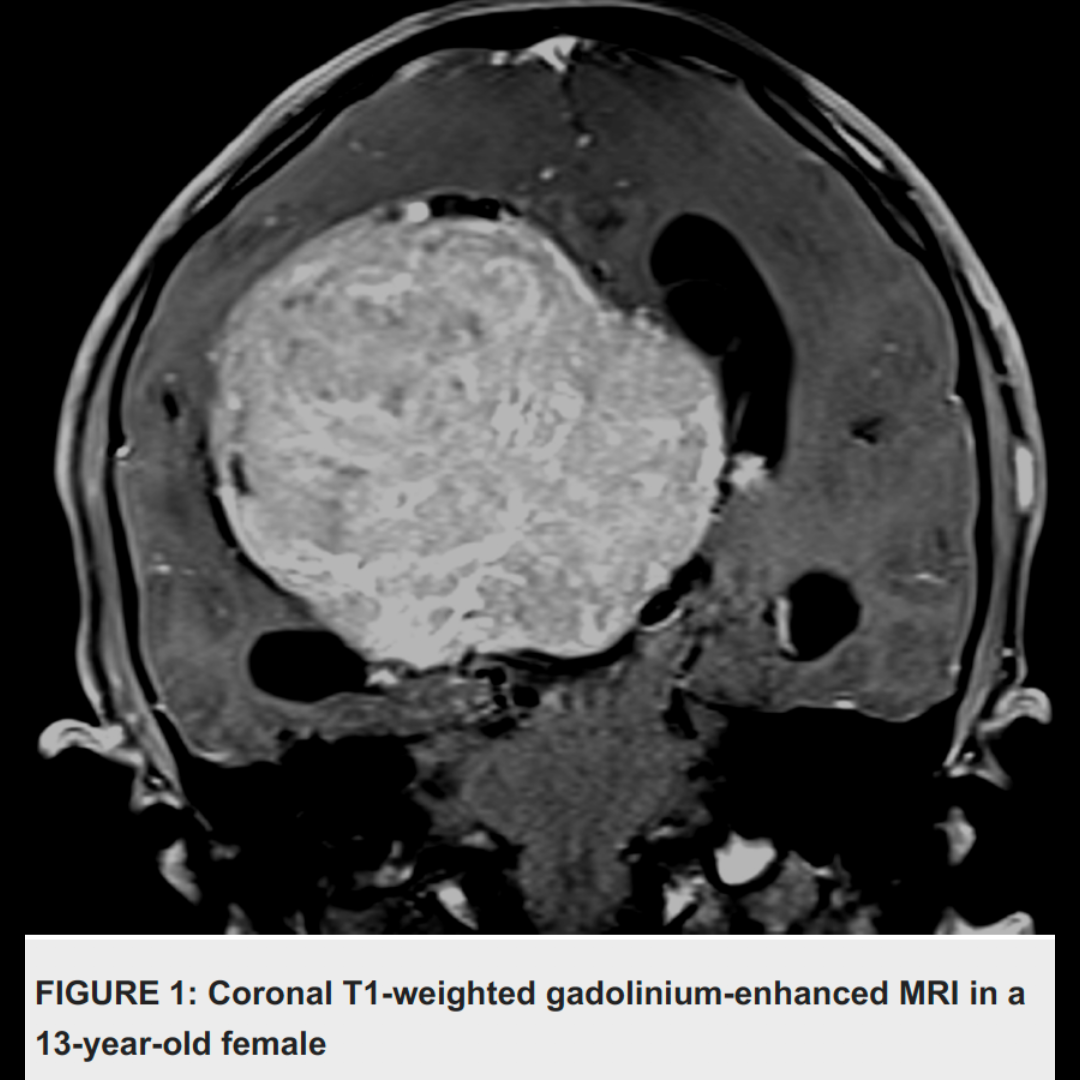
We present a case of MDR A. baumannii in a 13-year-old girl following parietal craniotomy for the resection of a right intraventricular meningioma. Several days after surgery, the patient presented with clinical, radiological, laboratorial, and microbiological evidence of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii ventriculitis. She was treated with IV colistin and then with combined intraventricular-IV colistin, with partial failure.
The combined treatment of IV tigecycline and associated intraventricular and intravenous colistin was started, and significant improvement was observed clinically and radiologically, with negative cultures after one week.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of a successful combination of intraventricular and IV colistin combined with IV tigecycline after a partial treatment failure with intraventricular and IV colistin alone.